VLSP 2023 Challenge on Vietnamese Mispronunciation Detection
Important dates
- August 14, 2023: Registration open
- Sep 25, 2023: Training dataset release and Registration close
- Oct 15, 2023: Public test set release (maximum of 20 submissions per day)
- Nov 5, 2023: Private test set release (maximum of 6 submissions)
- Nov 26, 2023: Technical report submission
- Dec 15-16, 2023: Result announcement - Workshop days.
I. Task description
One of the hardest parts of learning Vietnamese is pronunciation due to its complex tonal system. Different diacritics combined with a word can create various meanings. Therefore, with the new Vietnamese learner, pronunciation is significantly important. A Computer-Assisted Pronunciation Training (CAPT) system is used to automatically assist the learner.
In this shared task, participants will be provided a Vietnamese pronunciation dataset. Some of the utterances are purposefully recorded with random errors. The objective is to build a Vietnamese mispronunciation detection model to identify the incorrect phoneme-level pronunciation among the data.
II. Dataset
Participants will be provided with two datasets for detecting mispronunciation. The first dataset [1] contains augmented recordings of adults speaking pairs of single-syllable Vietnamese words (released by MachinaX). The second dataset [2] features recordings of children aged 5 to 7, either speaking or reading Vietnamese sentences in passages or dialogues (released by SoICT-HUST and the Vietnam Psycho-Pedagogical Association).
2.1 Data representation
Hierarchical structure of word in Vietnamese:
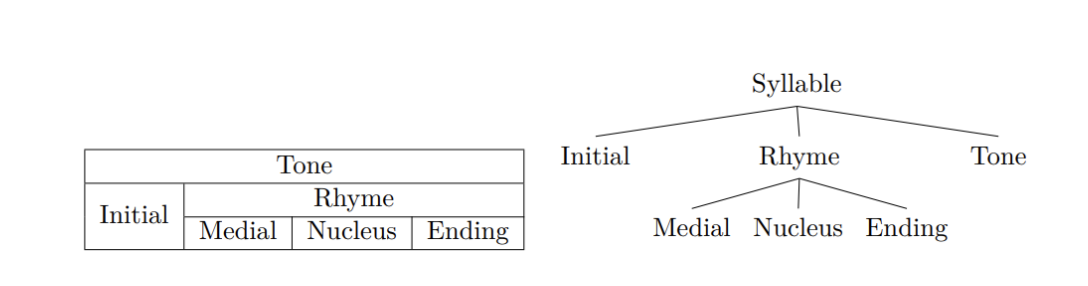
For example:
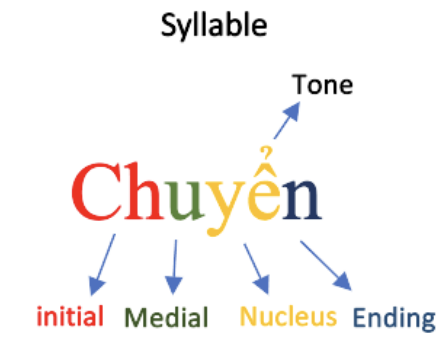
2.2 Dataset #1:
This dataset is created by a set of pairs of single-syllable words. Each pair of single-syllable words is formed by two Vietnamese words. Therefore, a pair may or may not have a meaning but be able to be pronounced. Each pair will be generated into 5 other variations, corresponding to overall 6 tones in Vietnamese: mid-level, high-rising, low-falling, high-rising-glottal, low-falling-rising, low-falling-glottal. These pairs of single-syllable words will later be recorded by a native speaker.
2.3 Dataset #2:
A group of native children who come from both kindergarten and primary schools participated in creating the dataset. All primary school children were recorded speaking spontaneously, while all kindergarten children were recorded reading sample sentences that we collected from various Vietnamese schoolbooks. There are 20 annotators who were trained to evaluate the entire dataset and mark any instances of incorrect or defective pronunciation.
2.4 Data format:
Each sample in the is a Vietnamese word that can have a mispronunciation error. We will provide the data set that contains the metadata information file and audios.
The file named “metadata.txt” that contains utterance ID, audio path, canonical syllables and transcription:
<ID>TAB<audio_path>TAB<transcripted_syllables>TAB<canonical_syllables>NEW_LINE
Participants will be provided two test sets: Public test and Private test and a Training set. The data that includes ~3700 utterances will be published for all. Otherwise, the private set will be privately used to fairly evaluate the system.
III. Regulations
- The use of external data and pre-trained models is strictly prohibited.
- Participants may use non-speech data (e.g., noise samples, impulse responses) for augmentation. They are also allowed to use pre-trained models, except those specifically designed for this task. All such usages must be clearly specified and shared with other participating teams.
- The task will have both public and private test sets. The final standings for all tasks will be determined based on the results from the private test sets. Teams might be asked to provide their source code to verify the final results.
IV. Evaluation metrics
The detection of pronunciation errors can be achieved by comparing the prediction sequence and the reference text sequence after alignment:
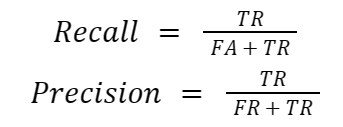
where:
- With canonical phones:
- TA (true acceptance) means the recognized phone sequence is matched with the reference text.
- FR (false rejection) means the recognized phone sequence differs from the reference.
- With mispronounced phones:
- TR (true rejection) means the mispronounced phones are detected
- FA (false acceptance) means failing to recognize the mispronounced phones.
The only metric to rank teams is F1 score.

V. References
[1]: Minh, N.Q., Hung, P.D. (2021). The System for Detecting Vietnamese Mispronunciation. In: Dang, T.K., Küng, J., Chung, T.M., Takizawa, M. (eds) Future Data and Security Engineering. Big Data, Security and Privacy, Smart City and Industry 4.0 Applications. FDSE 2021. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1500. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-8062-5_32
[2]: Huu, T.T., Pham, V.T., Nguyen, T.T.T., Dao, T.L. (2023) Mispronunciation detection and diagnosis model for tonal language, applied to Vietnamese. Proc. INTERSPEECH 2023, 1014-1018, doi: 10.21437/Interspeech.2023-364
VI. Organizers
- Nguyen Quang Minh, MachinaX R&D Technology Co Ltd
- Nguyen Thi Thu Trang, School of Information and Communication Technology, Hanoi University of Science and Technology
Contact to us at minh@machinax.net, huutu12312vn@gmail.com, thanh.pv.ds@gmail.com, trangntt@soict.hust.edu.vn















